
---
Heart Artery Disease
- Introduction
- Chest pain
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction)
- Assessment of the heart arteries
- Treatment of heart artery disease
Heart Artery Disease
Introduction
Disease of the heart arteries is most commonly due to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis refers to a process that causes the lining of the artery to become abnormally thickened. The thickening is often referred to as a "plaque".
The plaque of atherosclerosis is composed of a number of materials including deposits of cholesterol.
The factors that increase the risk of formation of plaque are termed "risk factors".
Significant disease refers to plaque that causes more than fifty percent narrowing of artery.
The heart arteries
The heart commonly has two main arteries, the left and right arteries. The left artery is usually much larger than the right artery. The left artery divides into two large arteries. Thus, the heart is often said to have three main arteries (the right and the two large branches of the left artery).
Left main stem disease
The term "left main stem" refers to that part of the left artery between at its origin and before its division into two large branches. Significant disease of the left main stem artery is an indication for heart bypass surgery.
Three vessel disease
When all three large branches of the heart are significantly diseased then this is termed "three vessel disease". Heart bypass surgery is often recommended when there is disease of all three arteries and with significant weakness of the heart's main pumping chamber.
Single or double vessel disease
This term refers to disease involving one or two large arteries, respectively. Routine heart bypass surgery does not prolonged survival in this situation.
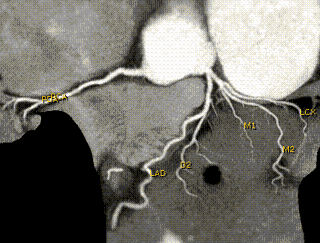
The image, above, of the heart arteries was obtained using a special fast XR machine (Multislice CT scanner). The solid white wavy lines are the arteries of the heart. The right heart artery is seen to the left. The left artery and its multiple branches are seen to the right of the image. In this particular instance, there was no significant disease of the heart's arteries.